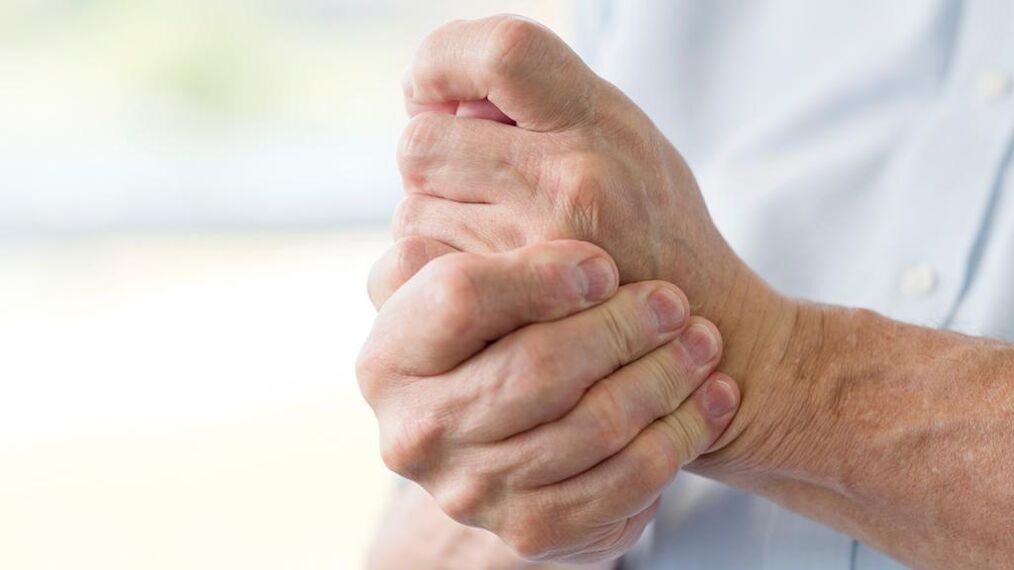
The human body has more than 300 joints: from the largest - the hips and shoulders, to the smallest - the joints of the fingers and toes. Each of them is important and necessary for a healthy and fulfilling life. At first glance, mild and unreasonable pain in the joints of the legs and arms may indicate a serious medical condition, with problems with the circulatory and metabolic systems. Therefore, it would be the right and timely decision to contact an orthopaedic specialist at the first manifestation of joint pain. After all, osteopathy, which views the body as a complex interconnected system of bones, joints, muscles and internal organs, gives the most logical statement of joint diseases and demonstrates the high efficiency of its treatment.
Numbness and pain in the hand. Causes and Diseases
Hand pain and numbness are often caused by dysfunction (damage) in the cardiovascular system. In addition, the cause may be cervical nervous system disease, compression of the nerves in the hand. In heart disease, numbness of the left hand is common, starting with a slight decrease in sensitivity of the little and ring fingers and gradually spreading along the extremities to the forearm, mainly affecting the interior.
Pain in the joints of both hands, along with numbness in the thumb and index (and sometimes middle) fingers, indicates involvement of the cervical spine, possibly from compression of a nerve, displacement of the disc or the vertebrae themselves.
Numbness in the fingertips most likely indicates a deficiency of vitamins A and B in the body. This symptom is most pronounced in late winter and early spring, when the body is as exhausted as possible.
At age 45 and older, numbness to the point of complete inability to move the hand, even with a small load on the joints (sewing, knitting, keyboard use) may indicate atherosclerosis of the blood vessels in the hand and damage to the elbow and shoulder joints.
Many age-related diseases and previous injuries manifest in the form of hand joint pain. Traction, bruises, and cracks in the navicular and lunate bones may not heal in one sitting, left unattended. The consequences of this careless approach may result in partial or complete loss of mobility. Plus, diagnosing fractures and fissures is simple—whether using an X-ray or during a visit to an osteopath. The latter can also help address the consequences of such injuries, eliminating possible bone displacement and vascular damage, pinching nerve endings that cause pain.
Occupational disease of hand joints
Hand joint pain can be caused by frequent overexertion, monotonous physical activity, adverse external effects on the joints. Most injuries and illnesses resulting from such exposures can be classified as occupational injuries.
So the joints of the hand often suffer from the following categories:
- People who spend a lot of time in front of the computer. In right-handers, the right hand is affected more often, and in left-handers, the left hand is more likely to be affected. Since the hand is always in the same position - on a computer mouse - the ligaments (tendons) and nearby nerves become swollen. Over time, increased wrist pain can lead to numbness and even the complete inability to move the hand. The disease is called - "tunnel syndrome";
- pregnant woman. "Tunnel syndrome" also manifests in them, becoming most noticeable after 3-4 months of pregnancy. Often, hand joint pain is preceded by swelling, which is characteristic of the third trimester. Combined with weight gain, they can cause damage to the wrist nerve. The pain varies from mild joint discomfort to complete numbness in the hands. Usually, after the child is born, the function of the joints returns;
- Pianist, tailor, laundromat, cleaner. Hand pain is limited to this area due to the constant pressure that falls primarily on the tendon muscles responsible for the work of the thumb. Early diagnosis of the disease makes it relatively easy to manage. The main thing is to contact an osteopath before the growth formation of scar tissue begins to change. This is usually preceded by significant joint pain, inflammation and swelling;
- Crane operators, carpenters, builders use jacking tools. The so-called Kienböck disease (avascular necrosis of the carpal bone) develops as a result of severe damage to the hand joints or routine microtrauma. The disease is caused by disrupted blood circulation in the wrist area, so the joints of the hand experience severe pain, and then changes and destruction of bone tissue begin to occur. Often, the joints of the hand of a human worker are affected.
Other causes of hand joint pain
Pain in the hand joints is not limited to the hand area. The shoulder and elbow joints are also frequently affected. Often, their lesions result from injuries to the hands and spine, as well as disease and age-related changes that result in thinning of the cartilage tissue in the joints. Treatment may vary in each case - depending on the complexity and severity of the disease. Only an experienced osteopath can diagnose the cause of hand pain, joint tightening, and other hand movement disorders.
Osteopathic Therapy for Hand Joint Pain
Hand joint pain is not always directly caused by damage to these joints themselves. Instead, the source of the disease is often far away from the hand. This is why only treatments aimed at eliminating the underlying cause can be effective. This is the method used by osteopaths. At the same time, the complex approach showed high efficiency in the case of hand pain, when manual techniques were combined with moderate physical activity, while correcting the patient's nutrition and affecting the main source of the disease.
During the first stage of treatment, the pain in the arm joints always stops. This makes the patient's body more sensitive to the effects of osteopathic therapy and allows him to completely relax during treatment. Since the session itself requires a considerable rest period (1-2 weeks) to allow the body to recover and adapt to the influence of the osteopath on its function, it is recommended to hold the joint in a fixed position during this period. Bras, various support bandages, etc.
After the pain in the arm joint is gone, the osteopath begins to relieve muscle spasms and remove blockages that interfere with normal blood circulation in the area near the joint and throughout the body. Restoration of blood supply to the affected area improves tissue nutrition, so pain does not return and the joint itself begins to gradually recover.
During the recovery phase, proper nutrition is very important, which will allow the body and damaged parts to obtain all the necessary trace elements, vitamins and nutrients. Due to the gradual renewal and recovery of the tissues, the joints of the hand lose mobility and not only the pain but also the numbness and discomfort are gone.
To maintain the improved state of the hand, the joints must be gradually loaded to consolidate positive tendencies and strengthen the muscles of the hand. Physiotherapy procedures and physiotherapy exercises should be carried out under the strict supervision of a specialist and should be standardized. If the pain returns to the joints of the hand, it is necessary to reduce the load.
At the same time as the hands are treated, the root causes of the disease are also affected - the spine, the cervical spine, the internal organs. Osteopathic techniques aim to improve blood supply and metabolism throughout the body, which of course has a positive effect on the work of all its systems. The benefit of turning to an osteopath in this situation is that while treating the pain in the hand, he can also relieve other, deeper conditions that have become the underlying cause of this pain.
Hand joint pain does not always affect the wrist area, so traditional treatments using symptomatic approaches may not work. An osteopath with a broader understanding of the problem can help in several sessions.