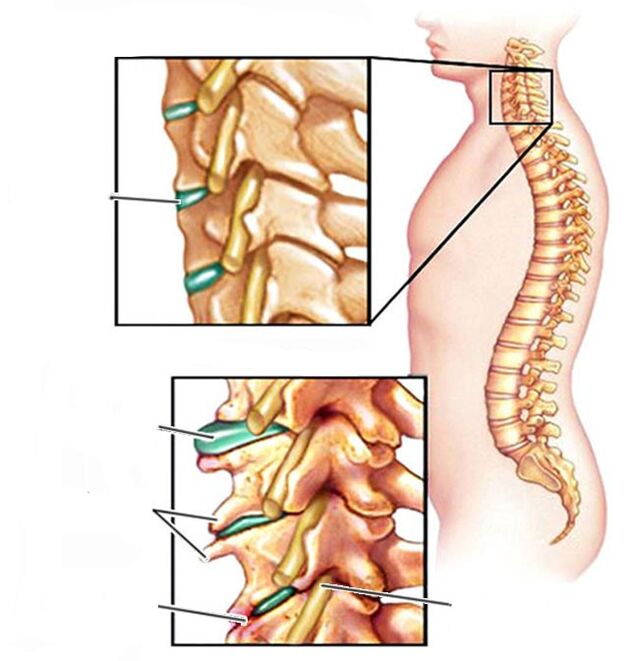
The diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis is based on a simple study-X-ray. In order to make the disease subside, a comprehensive method is needed to treat cervical osteochondrosis.
In order to make the disease subside, a comprehensive method is needed to treat cervical osteochondrosis.
Why does cervical osteochondrosis occur?
The pain has several local lesions: neck, head, shoulders. Weakness of the neck muscles can lead to the development of osteochondrosis. Due to improper posture, non-exercise and unnatural postures, some neck muscles will continue to be tense, while others will take excessive rest time. The spine will adapt to the unreasonable load at the cost of unhealthy. In cervical osteochondrosis, the following changes are recorded:
- Violation of blood and lymph flow;
- Lack of nutrition in the connective tissue of the intervertebral disc;
- The position of the vertebrae relative to each other is unstable.
The structure of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs is gradually destroyed. This process is irreversible, so you need to take care of your health on time and receive treatment immediately to treat the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, without having to postpone it until later. The reasons also include:
- Neck injury;
- Excess weight;
- Abnormal connective tissue
- Malnutrition and insufficient water intake.
Cervical osteochondrosis: symptoms
Main signs (vertebral body):
- pain. It can be pulled continuously, or it can appear in the resting position of the neck for a period of time and fall asleep in an uncomfortable posture. Severe pain makes the patient unable to move for a short period of time (lower back pain);
- Torticollis or difficulty in movement. Sometimes, turning or tilting the head can be so painful that people find a comfortable posture to minimize the pain and try to stay in it;
- Muscles are tense, stiff, and heavy;
- Clench your spine as you turn your head. Extravertebral symptoms of cervical chondropathy (involvement of nerves and surrounding tissues);
- Muscle inflammation;
- Headache, migraine, dizziness, sometimes accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- Pain in the back of the head, increased intracranial pressure, and a feeling of heaviness of the head; this symptom sometimes occurs so obviously that the term "head osteochondrosis" has taken root in patients. Obviously, headache is only a secondary manifestation of pathological changes in the skeletal system. It is correct to talk about cervical spondylosis rather than head osteochondrosis.
- Destruction of sensory organs: due to lack of nutrition in the brain, hearing and vision, speech impairment, tinnitus;
- Clavicle pain, arm stretched out to palm;
- The neck and arms are tingling and chills, and sometimes the fingers are tingling.
- Limit the range of motion of the arm (possibly on one side).
The dangerous consequences of cervical osteochondrosis: it must be treated!
If the degeneration does not stop, the following can be added to osteochondrosis:
- Nerve root pain caused by spinal nerve tension;
- Protrusion and hernia, compress the spinal cord and cause complete paralysis;
- Cervical cranial pain (cervix migraine, dystonia of vertebral artery syndrome);
- The formation of osteophytes on the vertebrae.
Treatment of cervical spine chondropathy
There is no cure for this disease with medicine. You can only use painkillers to eliminate the pain syndrome. But they always have side effects, so it is recommended to use them only in extreme situations. The symptoms and treatment of cervical osteochondrosis vary from patient to patient and require individualized treatment.
Doctors have a wealth of advanced technology reserves; they can choose the most effective and efficient one. Effective treatment of cervical osteochondrosis and its manifestations:
- Traction on the DRX robot-it can restore the correct position of the vertebrae without the risk of injury;
- Shockwave therapy-improve blood and lymph flow to the affected area, restore metabolism, relax muscles;
- Interstitial electrical stimulation-fights the complications of osteochondrosis, relieves the pain caused by the inflammation of the pinched nerve;
- HILT-laser therapy can relieve pain immediately.
The next step in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis symptoms is to restore blood supply and consolidate the correct position of the vertebrae. The rehabilitation process may require several times, including physical therapy, manual therapy, and the use of modern equipment. The more accurately the patient follows the expert’s advice, the more effective the technique will be. The final stage is within the patient’s responsibility:
- Correct lifestyle and nutrition;
- Regular exercise therapy;
- Positive attitude towards life and optimism.